Manual: Small RNA target prediction
The 'Small RNA Target Prediction' function can be launched by clicking corresponding button at the navigation bar of psRobot webpage (Fig. 1).

Fig. 1. Click the tab in the orange box to launch the small RNA target prediction function.
To find target relationship between small RNAs and mRNAs, users can either upload their small RNA and/or mRNA sequences or choose the preloaded small RNA and/or mRNA sequences to initiate the 'Small RNA Target Prediction' function (Fig. 2). The demo buttons above the textareas and selectboxes will fill them with the demo values. It is noticable the preloaded miRNA sequences from mirBase and the preloaded transcript libraries cannot be selected at the same time currently due to computational ability considerations, and the selection of each of them will disable the options of the other.
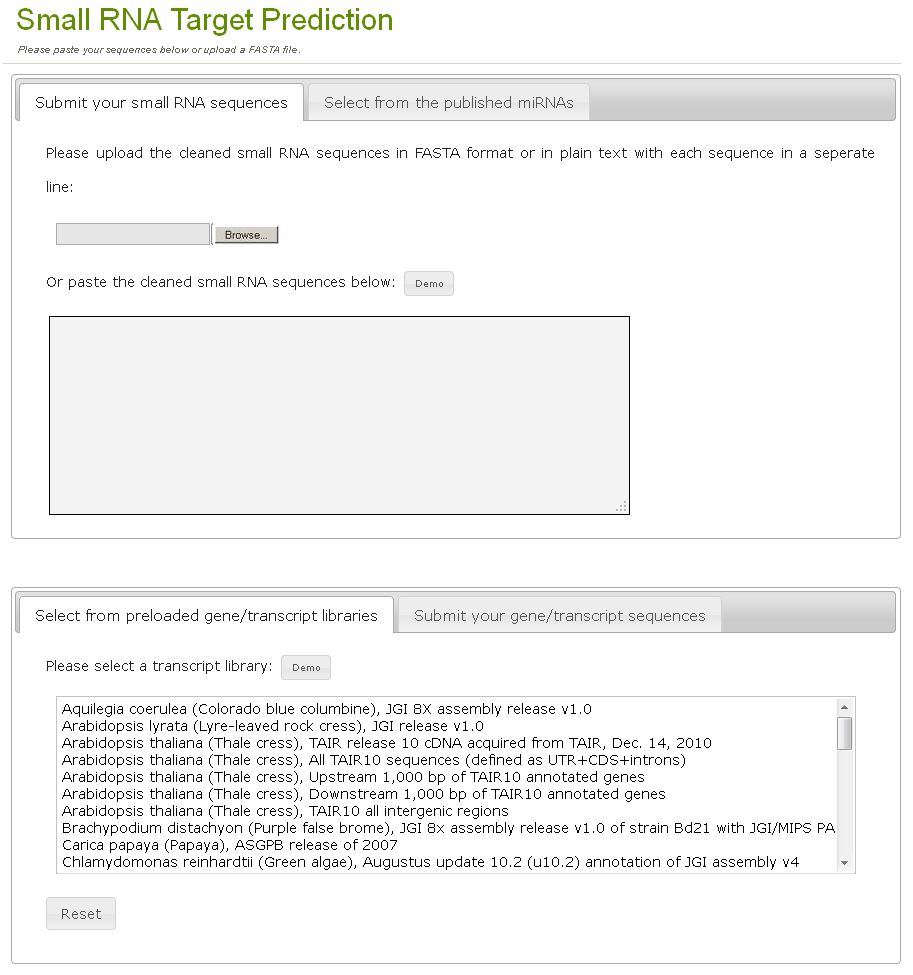
Fig. 2. The small RNA target prediction tool page.
We provide parameters for target prediction to make the stringency of the prediction tunable. There are also 3 sets of pre-set parameters. Click one of the "Strict", "Moderate" and "Loose" buttons will make one of the sets selected. The adjustable parameters for the 'Small RNA Target Prediction' function (Fig. 3) are:
- Target score threshold (0-5, lower is better): maximal allowed penalty score between small RNA and target alignment (lower is better). The scoring system for small RNA target presiction is the following: the penalty score for a mismatch or gap in small RNA and target alignment is 1, the penalty score for a G:U pair is 0.5. Mismatches, gaps or G:U pairs will receive a full penalty score if they occur at the essential sequence region (can be defined by the following 2 parameters) of small RNAs, and half of the above mentioned score if they occur outside of the essential sequence region.
- Five prime boundary of essential sequence (0-1): the five prime boundary of the essential sequence that the perfect pairing between essential sequence to targets is important for small RNAs to execute their functions.
- Three prime boundary of essential sequence (15-31): the three prime boundary of the essential sequence that the perfect pairing between essential sequence to targets is important for small RNAs to execute their functions.
- Number of gaps permitted (0-5): the number of total gaps permitted in the alignment between small RNAs and their targets.
- Position after which with gaps permitted (1-30): the region where no gaps between small RNAs and targets are permitted in their alignment. For example, the value "13" means gaps are only allowed to occur after the 13th nucleotide.
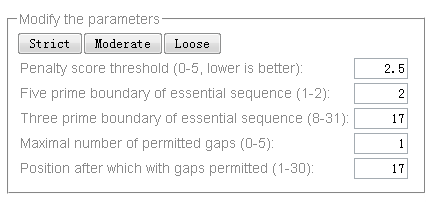
Fig. 3. Parameter setting options of the small RNA target prediction tool.
Output of the 'Small RNA Target Prediction' function:
The results of target prediction are listed in a table. The table is sortable by clicking each column name, and searchable by the magnifier button in the bottom left (Fig. 4). Descriptions of the ten columns are:
- sRNA ID: Identifiers of query small RNAs.
- Target ID: Identifiers of small RNA target genes/transcripts.
- Score: Penalty score of the small RNA and target alignment (see scoring method).
- Alignment: The sequence alignment between small RNAs and their targets. Symbols used are: '|' for paired nucleotide; '-' for gaps; ':' for G:U pair.
- Annotation: The annotation of target sequences.
- Mul: The number of target sites on each target gene/trnascript. Sometimes there are multiple target sites of the same small RNA on a gene/transcript.
- Conservation: The conservation status of the target site sequence among eight species (Arabidopsis thaliana, Carica papaya, Vitis vinifera, Populus trichocarpa, Oryza sativa, Brachipodium distachyon, Zea mays and Sorghum bicolor). Click the hyperlink will show the multiple alignment of the target sequences and alignments between small RNAs and targets (Fig. 5a).
- Degr: Degradome data of each target site. This column represents the cleavage information within or near the predicted small RNA target site of the target transcript. The number shown is the highest number of cloned reads within/near the small RNA target position. 'N/A' means no degradome data available for the target genes. Click the hyperlink to view the detailed distribution of the cleavage sites along the target region (Fig. 5b).
- Biog: The expression change of target genes in small RNA biogenesis related gene mutants as compared to wildtype plants. The numbers shown are log2 transformed fold change of target genes as compared to wildtype plants. If multiple datasets are available for a gene, the highest fold change will be listed. Click the hyperlink brings up the webpage showing the detailed expression change of targets in each mutant (Fig. 5c).
- KnoT: Link to PubMed related publications if a predicted target is already predicted or validated to be a target of the query or other small RNAs. Information included is manually collected from published papers.
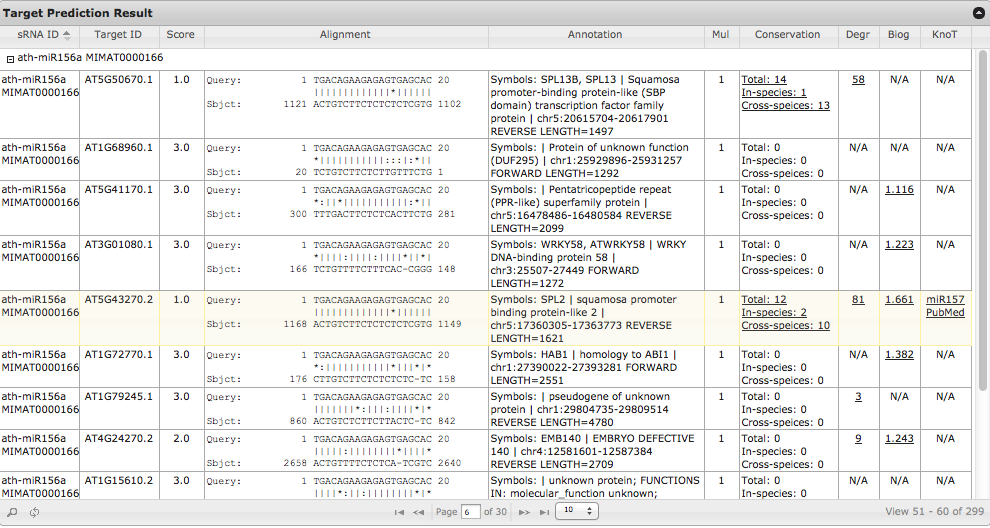
Fig. 4. The result page of small RNA target prediction tool. Click here for an interactive sample output.

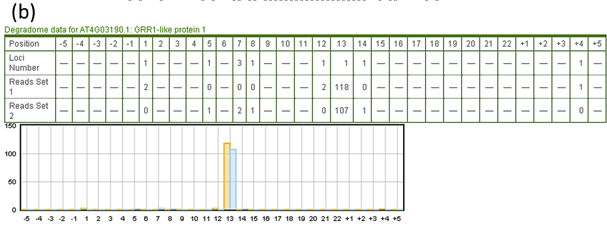
- Putative target region of query small RNAs are numbered from 1 to the length of the small RNA in the position row. Upstream and downstream neighbouring sequences are shown as negative and positive numbers. 'Loci number' represents the number of genomic locations of a degradome read. Numbers in the 'Reads Set' row(s) are noramlized clone count (RPM, reads per million) of each degradome sequence starting from each corresponding position.
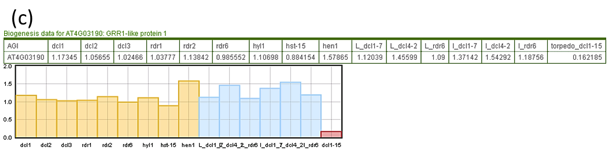
Fig. 5. The detailed results of small RNA target prediction tool.
Appendix I: Degradome datasets used for 'Small RNA Target Prediction Function'.
| Species | Dataset | Tissue | GEO Dataset |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arabidopsis thaliana | reads set 1 | WT inflorescence | GSE11094 |
| reads set 2 | xrn4 inflorescence | GSE11094 | |
| Oryza sativa | reads set 1 | seedling | GSE17398 |
Appendix II: Gene expression microarray data of small RNA biogeness related gene mutants used for 'Small RNA Target Prediction' function.
| Species | Sample Name | Sample Type | Tissue | GEO dataset |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arabidopsis thaliana | dcl1 | dcl1-7 | Flower stages 1-12 | GSE2473 |
| dcl2 | dcl2-1 | Flower stages 1-12 | GSE2473 | |
| dcl3 | dcl3-1 | Flower stages 1-12 | GSE2473 | |
| rdr1 | rdr1 | Flower stages 1-12 | GSE2473 | |
| rdr2 | rdr2 | Flower stages 1-12 | GSE2473 | |
| rdr6 | rdr6 | Flower stages 1-12 | GSE2473 | |
| hyl1 | hyl1 | Flower stages 1-12 | GSE2473 | |
| hst-15 | hst-15 | Flower stages 1-12 | GSE2473 | |
| hen1 | hen1 | Flower stages 1-12 | GSE2473 | |
| L_dcl1-7 | dcl1-7 | Rosette leaves (5-8) | GSE3011 | |
| L_dcl4-2 | dcl4-2 | Rosette leaves (5-8) | GSE3011 | |
| L_rdr6 | rdr6 | Rosette leaves (5-8) | GSE3011 | |
| I_dcl1-7 | dcl1-7 | Inflorescence stages (1-12) | GSE3011 | |
| I_dcl4-2 | dcl4-2 | Inflorescence stages (1-12) | GSE3011 | |
| I_rdr6 | rdr6 | Inflorescence stages (1-12) | GSE3011 | |
| Torpedo_dcl1-15 | dcl1-15 | Torpedo staged embryos | GSE24887 |